Background
Before we dive in to the tutorial
- Sign up for an OpenCage geocoding API key.
- Play with the demo page, so that you see the actual response the API returns.
- Browse the API reference, so you understand the optional parameters, best practices, possible response codes, and the rate limiting on free trial accounts.
Installing the MCP server on your computer
-
Clone the git repository
The MCP server code is open source and hosted on GitHub.
git clone git@github.com:OpenCageData/opencage-geocoding-mcp.gitor
git clone https://github.com/OpenCageData/opencage-geocoding-mcp.git -
Switch into the repository directory
cd opencage-geocoding-mcp -
Install dependencies
You will need to have node installed. Then run:
npm install -
Configure LLM Client
You need to share your MCP configuration with your LLM client, such as Claude Desktop or Cursor. The configuration details are how your LLM client knows the MCP is available, how to call it, and which OpenCage geocoding API key to use.
Copy this JSON and update it for your installation:
{ "mcpServers": { "opencage-geocoding": { "command": "node", "args": ["/ABSOLUTE/PATH/TO/opencage-geocoding-mcp/build/index.js"], "env": { "OPENCAGE_API_KEY": "YOUR-API-KEY" } } } }Be sure to edit the
argsentry so it points to the directory where you installed the MCP. -
Where to find your configuration:
-
Claude Desktop:
On MacOS the config file should be
~/Library/Application Support/Claude/claude_desktop_config.jsonbut you can also navigate to the file via the menu. SelectSettings > Developer > Edit Config -
Cursor:
Open Cursor Settings and navigate to MCP Tools. Click the
Add Custom MCPbutton, paste your edited JSON, and save the file.
-
Claude Desktop:
-
Restart the LLM client
So that the new configuration is used.
Using the MCP
You should now be able to make geocoding requests from within Claude Desktop simply by formulating a prompt involving geocoding.
For example try
geocode the coordinates 52.5432379, 13.4142133
Note that the first time the MCP is used you will be prompted to give permission.
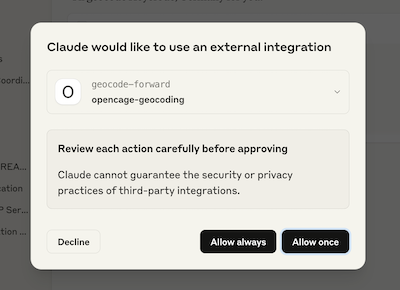
The LLM should recognize that this request can be answered by the MCP and hand the query off to our geocoding API
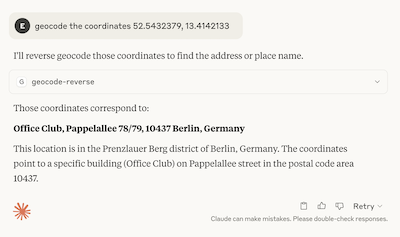
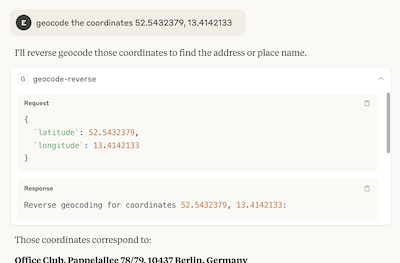
You can expand the response to get more details, including the actual API request if you want to see the full JSON response returned by the API.
Some example prompts
-
"Where is Les Vans, France? Which Department is it in?" -
"What are the coordinates of Trafalgar Square, London?" -
"What are the coordinates of Pappelallee 78, Berlin?" -
"What is the address at -36.84694, 174.73662?"
Other commands
We also provide the following two commands:-
"geocoding-assistant"provides an overview of how the MCP works and available commands
-
"get-opencage-info"If you are a free-trial user or one-time plan customer this command checks your current API usage and rate limits (subscription customers don't have hard limits, so this information is not returned for them), and also confirms that the API is working well (returning status 200).
Send us your feedback
As with all things in the realm of AI, this space is evolving very quickly. It's not currently entirely clear what the exact best practices are, nor what information we should make available to the LLM. Please let us know how you are using the MCP and if there are things we can change to make the service more useful.
2,500 geocoding API requests/day - No credit card required